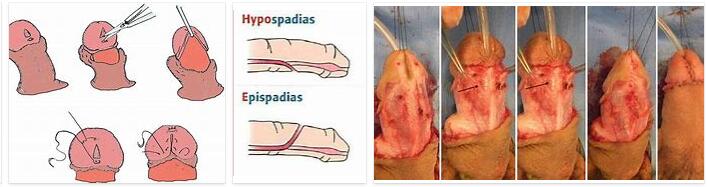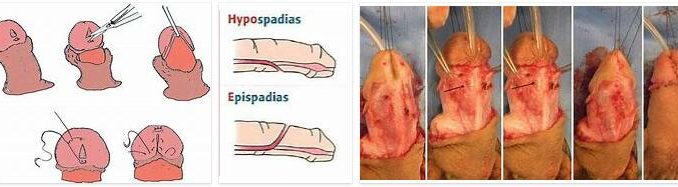
Hypospadias is a malformation in the urogenital tract. In affected boys, the urethra does not sit at the tip of the penis. This leads to various functional limitations that can be treated surgically.
What is hypospadias?
According to abbreviationfinder, hypospadias can primarily be recognized by the shortened urethral opening. In boys, the urethral opening usually ends under the glans, in girls it ends in the vaginal wall.
In hypospadias, the urethral opening is on the underside of the penis and does not open at the tip of the penis. The urethra is shortened.
Depending on the severity, the urethra can end below the glans or even at the perineum. This makes it difficult for the affected boy or man to urinate standing up because the stream runs backwards. Hypospadias is one of the most common genetic malformations of the male urogenital tract. It often goes hand in hand with an enormous psychological burden on the parents and the affected boy.
A distinction is made between glandular, penile and scrotal hypospadias. The mildest form, glandular hypospadias, is the most common. The urethral opening is on the underside of the glans. In penile hypospadias, the urethra opens into the shaft of the penis, which requires treatment and can lead to functional limitations.
The most severe form is scrotal hypospadias, in which the opening of the urethra is at the base of the penis or the perineum.
Causes
Hypospadias is a hereditary malformation. Around the 14th week of pregnancy, the formation of the urethra is usually complete. Up to this period, however, developmental disorders or interruptions in development can occur. The severity of hypospadias depends on the developmental stage at which the disorder occurs.
In addition to the hereditary factor, endocrine and environmental influences also play a role. Thus, a defect in the receptors for testosterone could be detected. If the mother takes the hormone progesterone during pregnancy, this can increase the risk of the baby developing hypospadias.
In addition, babies born underweight seem to suffer from hypospadias more often than average. However, the exact factors that lead to this clinical picture are not yet fully understood.
Symptoms, Ailments & Signs
Hypospadias can primarily be recognized by the shortened urethral opening. In boys, the urethral opening usually ends under the glans, in girls it ends in the vaginal wall. Individuals suffering from hypospadias have problems urinating and ejaculating. Pain and burning can occur when urinating and during intercourse, which usually subsides after a few seconds to minutes.
Furthermore, the malformation manifests itself through repeated infections and inflammations in the affected area. Those affected are generally severely restricted in their everyday lives and, in addition to the actual symptoms, also suffer from avoidance behavior and the consequences that result from it. Regular urinary retention can cause inflammation and, in the worst case, lead to incontinence.
Avoiding sexual intercourse also has psychological problems as a result. Those affected often feel extremely uncomfortable with the disease and withdraw from social life. The often chronic symptoms can cause psychological problems in the patient and lead, for example, to the development of inferiority complexes and depressive moods. For this reason, hypospadias must be diagnosed early and corrected as part of a surgical procedure.
Diagnosis & History
The treating urologist makes the basic diagnosis after a detailed physical examination. After that, in most cases, a sonography of the urethra is ordered. This also serves to clarify the degree of severity.
If the ultrasound examination is abnormal, a urogram is subsequently made. This is a contrast medium X-ray of the kidneys and urinary tract. In addition to these diagnostic measures, a voiding cystourethrography (MCU) can also be performed, in which the bladder is X-rayed before and after urination. As part of the diagnosis, it is also important to determine the severity of the hypospadias.
Basically, the course of hypospadias is absolutely positive with the right therapy. In many cases, the malformation can be corrected both cosmetically and functionally by taking appropriate measures.
Complications
Hypospadias causes the patient to experience discomfort in the genitals. In most cases, the patient suffers from discomfort during ejaculation and urination. This can lead to severe and burning pain that has a negative impact on everyday life. In addition, most men experience pain during sexual intercourse.
This pain can often lead to the development of psychological problems, leading to inferiority complexes or reduced self-esteem. Depression and other mental health problems can also occur. Hypospadias does not always need to be treated.
If the patient does not suffer from severe symptoms or does not feel restricted in his everyday life, then treatment does not necessarily have to take place. In this case, there are no complications. Treatment is necessary if the hypospadias leads to pain or severe psychological complications.
This usually requires an operation. There are no particular complications with this procedure either. In rare cases, the interfaces can become inflamed after the operation and must therefore be treated with the help of antibiotics. Life expectancy is not affected by hypospadias.
When should you go to the doctor?
Hypospadias is usually diagnosed immediately after birth. Whether further visits to the doctor are necessary depends, among other things, on the severity of the malformation and any accompanying symptoms. A slight urethral opening can be closed immediately after birth and only requires a few check-ups afterwards.
Major malformations, possibly associated with problems with urination and ejaculation, require comprehensive medical attention. Parents should take the child to the doctor if they complain of painful urination or show symptoms of fever. If the urethral opening becomes inflamed, further medical treatment is indicated. The affected person should be taken to a urologist immediately.
Early treatment reduces the risk of serious complications. Therefore, hypospadias should be clarified and treated as soon as possible, regardless of whether there are other symptoms. Children of mothers who take the hormone progesterone during pregnancy are particularly likely to be born with hypospadias. That is why expectant mothers who regularly take medication should speak to the doctor regularly and have the health of the child checked.
Treatment & Therapy
In mild cases of glandular hypospadias, no therapeutic intervention is usually necessary. Not infrequently, those affected with very mild forms of their hypospadias are not even aware.
However, if there are functional limitations, a surgical intervention is usually recommended. This ideally takes place from the first year of life of the affected boy. If the urethra is narrowed, an operation may be necessary even in infants. It is a complicated operation that can take several hours. The operation always takes place under general anesthesia.
There are various surgical approaches to correct hypospadias, depending on the severity of the malformation. Surgeons must also be aware of other urogenital tract malformations commonly associated with hypospadias. These include malformations of the erectile tissue in the penis or a curvature of the penis shaft.
It is not uncommon for there to be a split prepuce, which means that the foreskin is longer on one side and missing on the other side of the penis. During an operation, the urethra is placed at the tip of the penis. This is intended to enable normal urination or a normal erection. The surgeons also try to straighten the penis.
Prevention
Since hypospadias is a genetic or endocrinological malformation in the urogenital tract that occurs during early pregnancy, it cannot be prevented.
Aftercare
If the hypospadias has been treated, small bruises and swelling can develop. However, these healed after about four weeks. The operated children need regular follow-up appointments. They usually stay in bed for two to three days and keep the bandage on for three to seven days. After carefully removing and clamping the abdominal wall catheter, the child is allowed to urinate normally again.
Depending on the treatment method, the healing process may also take a little longer. Chamomile baths accelerate healing. The penis should be restored after four to six weeks at the latest. During the check-ups, the doctor makes sure of the patient’s condition.
Immediately after the operation, the children often feel slight pain. When the penis has healed, a scar is left that runs in a ring under the glans and sometimes along the underside. This shows the similarity with classic circumcision.
Follow-up care at home includes some caution with walking and other movements. Children often automatically take care not to move too vigorously. But parents can also make sure that their children do not do sports too early. The one-week sick leave is an important support in this context.
You can do that yourself
If there is only a slight malformation in the area of the glans, hypospadias does not have to be treated in most cases. Nevertheless, pain can occur when urinating and later in life during sexual intercourse, which, if the symptoms are minor, can be treated with mild painkillers from the pharmacy.
Surgery may be necessary for more severe symptoms. After such an operation, those affected can promote recovery by paying attention to appropriate hygiene measures and resting the area where the operation took place for a few days. Activities that could put a strain on the penis and genital area in general should be avoided in the initial period after the procedure.
Since an operation usually takes place in the first two years of life, the parents must watch out for any abnormalities and contact the responsible doctor if there are signs of pain or similar symptoms. Further measures are limited to taking good care of the operation scar in order to prevent the formation of a larger scar. The child should be informed as well as possible about the reasons for the procedure.