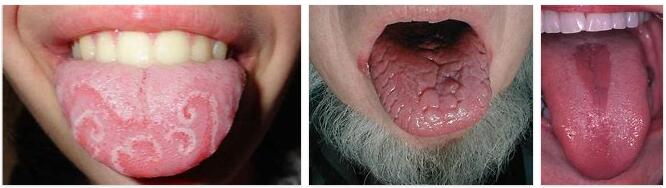
Glossitis is understood to mean both acute and chronic changes to the entire body of the tongue. Tongue inflammation is not limited to a specific age or gender, but can affect anyone.
What is glossitis?
Glossitis, or inflammation of the tongue, can affect the surface, mucosa, and muscle of the tongue. The entire tongue is inflamed, plaque and discoloration are often visible on its surface.
According to abbreviationfinder.org, the tongue may burn and become greatly enlarged. The swelling and burning vary in intensity, making speaking and swallowing difficult. Depending on the trigger of the inflammation, itching may also occur.
The loss of the sense of taste is rather rare, but it does happen. Such an inflammation is of course quite unpleasant, but in most cases the entire health balance is not disturbed.
Causes
There are many causes of glossitis. In most cases, however, an injury while eating is the cause of this inflammation – you bite your tongue. Such problems also arise from piercings. Anyone who wears a denture that does not fit properly and therefore rubs can also expect glossitis.
Heavy smokers are also at risk. But the tongue can not only become inflamed by external influences. Food allergies or hypersensitivity to other substances can become visible through the symptoms mentioned. The reason for the glossitis can also be a fungal infection. In the case of serious weaknesses in the immune system, for example in the case of AIDS, the body can react by inflaming the tongue.
This also applies to serious illnesses such as tongue cancer. Tongue inflammation can occur with any disease that alters the normal flow of saliva. Last but not least, permanent burning of the tongue can indicate manifest nervous disorders.
Symptoms, Ailments & Signs
Glossitis can present with a variety of symptoms. Pain and swelling of the tongue are typical of the disease. The characteristic burning tongue is usually accompanied by [8taste disturbances]], [8difficulty swallowing]] and itching. A foul-smelling coating often forms on the tongue. Many of those affected also feel an increasing itching in the mouth.
If the glossitis is not treated, other symptoms can develop over time. As a result of the lack of food intake, there can be an undersupply, which can manifest itself, among other things, in exhaustion and dizziness. Bleeding in the mouth can also occur. Externally, glossitis can primarily be recognized by the reddened tongue.
In individual cases, blisters and nodules form on the tongue, which are very painful when touched. In children, glossitis can cause other symptoms, such as nausea and vomiting or temporary personality changes. The sometimes very severe pain can lead to outbursts of anger or apathy, for example.
Parents who notice such signs should take the child to the pediatrician immediately. Although glossitis is not a serious disease, early diagnosis and treatment can reliably prevent major complications.
Diagnosis & History
The diagnosis of glossitis usually does not pose any major problems for the doctor. If the patient describes the symptoms, it is not difficult to draw conclusions about the present disorder. The doctor can look at the mouth and tongue and thus confirm his suspicion.
However, it becomes significantly more difficult when the tongue infection is a symptom of another disease. Then the trigger must be found with detailed investigations. This allows the doctor to take a smear test to find out if there is a fungal infection.
If the inflamed tongue is the result of an allergy, this can be found out using suitable test methods ( patch test or prick test ). In most cases, food and oral care products are checked.
Complications
Both sexes are usually equally affected by glossitis. The disease can also occur in children. This leads to increased complaints and symptoms on the train. First and foremost, the patient suffers from a strong burning sensation on the tongue. The tongue may also be swollen.
The burning leads to disturbances in the absorption of food and liquid, so that it is not uncommon for underweight or dehydration to occur. The glossitis reduces the quality of life enormously. There are also taste disorders and problems with swallowing. This can be dangerous, especially for children, and lead to choking.
A coating forms on the tongue, which can lead to unpleasant odours. The everyday life of those affected is enormously restricted by the glossitis. Psychological complaints can also occur due to the pain and limitations.
As a rule, a relatively simple treatment of glossitis is possible. This is done with the help of antibiotics or mouthwashes and quickly leads to a positive course of the disease. There are no further complications. In the event of an allergy or intolerance, the substance in question must be avoided.
When should you go to the doctor?
If your tongue or mucous membranes in your mouth swell, you should see a doctor. Report an unusual taste in the mouth or changes in taste perception to a doctor. A furry or very slippery feeling on the tongue also requires a doctor’s visit.
If the sufferer suffers from pain in the mouth, this is considered unusual and should be investigated. Medical treatment is also necessary as soon as there are impairments in the formation of sounds. Restricted or unclear speech formation must be medically clarified. If you refuse to eat or drink because of the symptoms, you should see a doctor. If the symptoms lead to weight loss or a feeling of dryness inside the body, there is an urgent need for action.
There is a risk of an acute health-endangering condition that requires medical care as soon as possible. A doctor should be consulted if you have difficulty swallowing, problems with an existing denture, a feeling of tightness in your mouth or itching. Bad breath, a coating on the tongue or discoloration of the tongue should be examined and treated. If a burning sensation is felt inside the mouth, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Treatment & Therapy
Treating simple glossitis is not particularly difficult. In most cases, no special therapy is necessary. The inflammation heals quickly by rinsing the mouth and throat.
Rinses with sage or salt water are suitable here. In the chronic form of glossitis, the cause plays a decisive role. If an infestation with fungi was the cause of the tongue infection, the doctor can prescribe an antifungal, i.e. a remedy against the fungal infection. If bacteria are responsible for the disease, an antibiotic can help. If there is an allergic reaction, the triggering substance must be avoided.
The healing process can also be supported with herbal remedies. Marshmallow leaves or marshmallow roots, witch hazel or buckhorn can be used as a tea or gargle solution to alleviate the symptoms and contribute to healing. The chances of healing from glossitis are generally very good. If the causes of the tongue problems can be identified, the inflammation can heal within a few days.
Outlook & Forecast
The chance of healing when glossitis is diagnosed is extremely good. In some cases, there is improvement even without treatment. The illness usually lasts a few days. It depends on whether the upper or lower layers are affected.
Patients can make a contribution to stop the characteristic burning tongue. You should refrain from nicotine during treatment. Spicy foods should also be avoided. Allergy sufferers also refrain from consuming foods that trigger a reaction.
If doctors only try to reduce the acute burning sensation in the tongue, relief is not always satisfactory. Proper diagnosis leads to a final cure. What used to cause problems is now regularly carried out correctly. It must be clarified where the inflammation of the tongue mucosa comes from. Oral antibiotics and topical medications provide excellent results in many cases.
If you start the wrong treatment, the symptoms are only reduced for a short time. In the worst case, the inflammation spreads to the teeth and gums. Feverish states can then also occur. The taste buds are temporarily disturbed. Swallowing and speaking difficulties are possible.
Prevention
Preventive measures can prevent glossitis. Wearers of dentures should make sure that the prosthesis fits properly and is well adjusted. If the immune system is weakened by an illness, special attention should be paid to oral hygiene.
Tongue piercing wearers must also pay great attention to the hygiene of their teeth and mouth. Heavy smokers should implement a reduction in their tobacco consumption. In general, rinses with disinfectants and anti-inflammatory agents are a good choice to prevent glossitis.
Aftercare
In the case of glossitis, the options for aftercare are very limited. As a rule, the person affected is always dependent on medical treatment first in order to relieve the symptoms and limit the disease. A self-healing of the glossitis does not usually occur.
In most cases, the patient is dependent on rinsing the oral cavity with various agents. These can either be purchased at the drugstore or directly prescribed by a doctor. It is important to ensure that it is used regularly in order to completely limit the glossitis.
Even after the symptoms have subsided, further treatment is usually necessary to completely limit the glossitis. In some cases, however, the symptoms can reoccur, so that further treatment is necessary. Proper oral hygiene is also important and should always be observed.
In severe cases, glossitis is treated with antibiotics. It is important to ensure that it is taken regularly. Antibiotics should not be taken with alcohol. Parents must ensure that children take it regularly and correctly. As a rule, glossitis does not reduce the patient’s life expectancy.
You can do that yourself
Glossitis can usually be treated by those affected themselves. The inflammation heals quickly if the mouth and throat are treated with a suitable rinse. Rinses with salt water, sage or chamomile are suitable, for example.
The chronic form of glossitis can also be self-treated, depending on the cause identified. However, the doctor should always prescribe an antifungal, the effects of which can then be supported by arnica and other natural medicine and homeopathic preparations.
The recovery can also be accelerated by herbal remedies. Among other things, marshmallow leaves or marshmallow roots as well as buckhorn and witch hazel have proven themselves, which can be taken as a gargle solution or tea and usually relieve the symptoms quickly. In the event of an allergic reaction, the most important measure is to avoid the triggering substance.
If the cause is not known, a complaint diary should be created. This allows the doctor or patient to determine the trigger themselves and take targeted countermeasures. If the symptoms have not subsided after two weeks at the latest, it is advisable to visit the responsible doctor again.